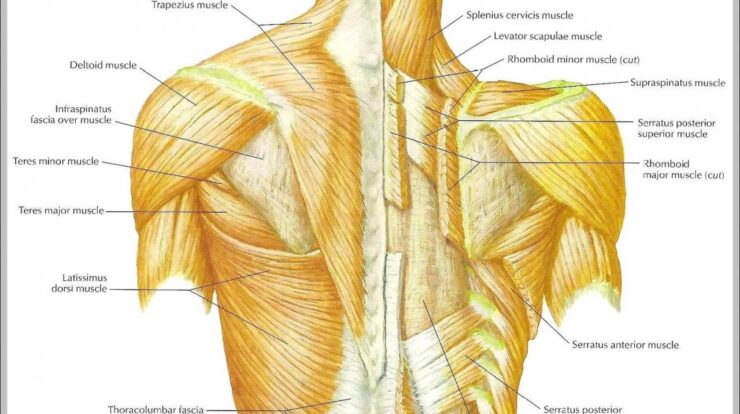
Back muscles, the unsung heroes of our musculoskeletal system, play a pivotal role in our overall movement, posture, and well-being. Understanding their anatomy, developing targeted exercises, and fueling them with proper nutrition is essential for achieving optimal back health and fitness.
If you’re experiencing lower back pain, it’s essential to seek medical advice. However, there are also exercises to relieve lower back pain that can help manage discomfort. These exercises focus on strengthening the muscles around the lower back, which can provide support and reduce pain.
From the powerful latissimus dorsi to the stabilizing trapezius, this guide will delve into the intricacies of back muscles, empowering you with knowledge to maximize their potential.
Anatomy and Physiology of Back Muscles
The back muscles are a complex and intricate group of muscles that play a crucial role in overall body movement, posture, and spinal stability. Understanding their anatomy and physiology is essential for maximizing their development and minimizing the risk of injuries.
As Mother’s Day approaches, many are sending happy mothers day wishes mom to express their love and gratitude. Mothers play a crucial role in our lives, and it’s important to celebrate them on this special day. Whether you’re looking for happy mothers day wishes for all moms or happy mother’s day greetings , there are many thoughtful ways to show your appreciation.
Some people prefer to create happy mothers day wishes for all moms images , which can be a lasting keepsake.
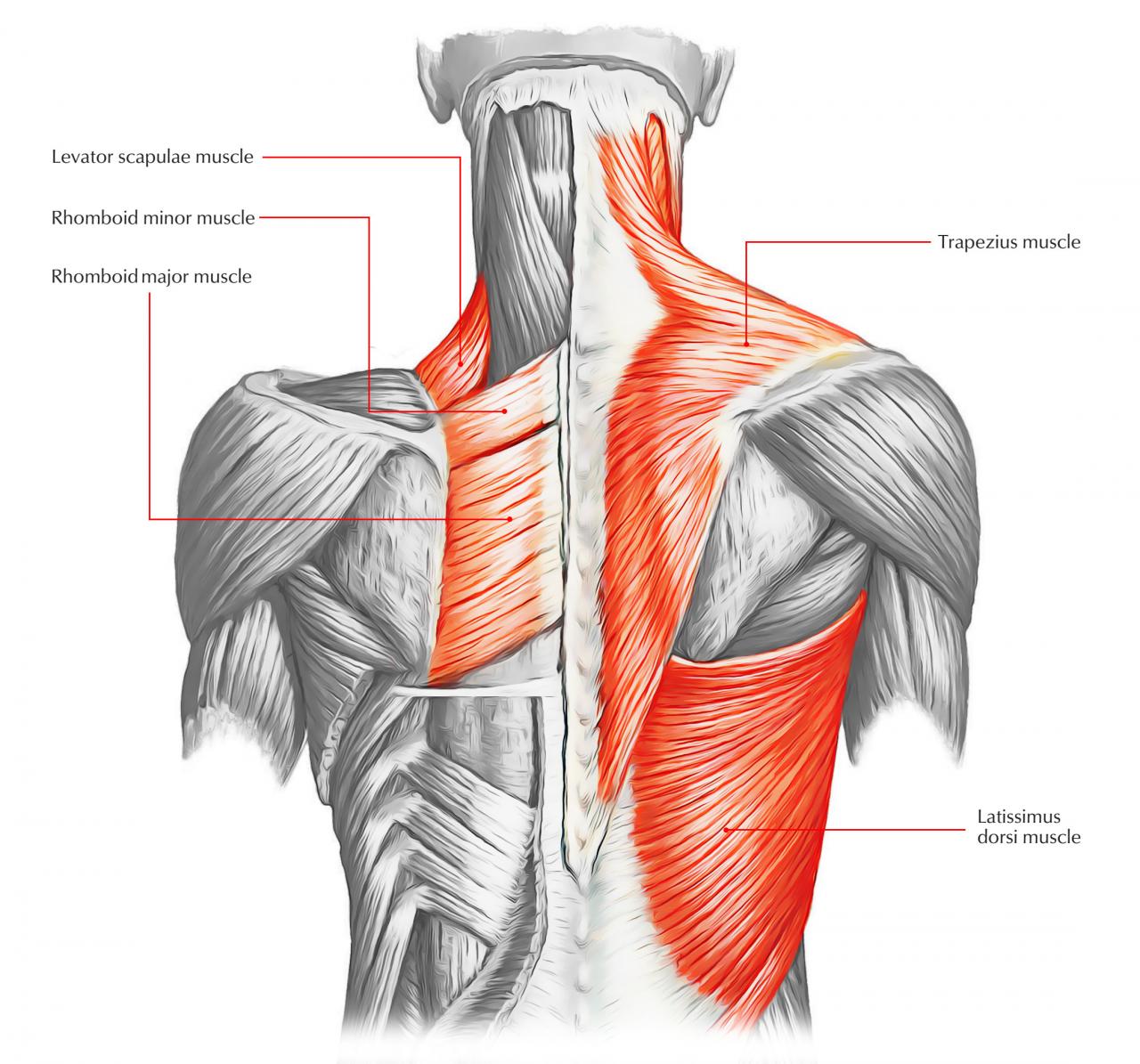
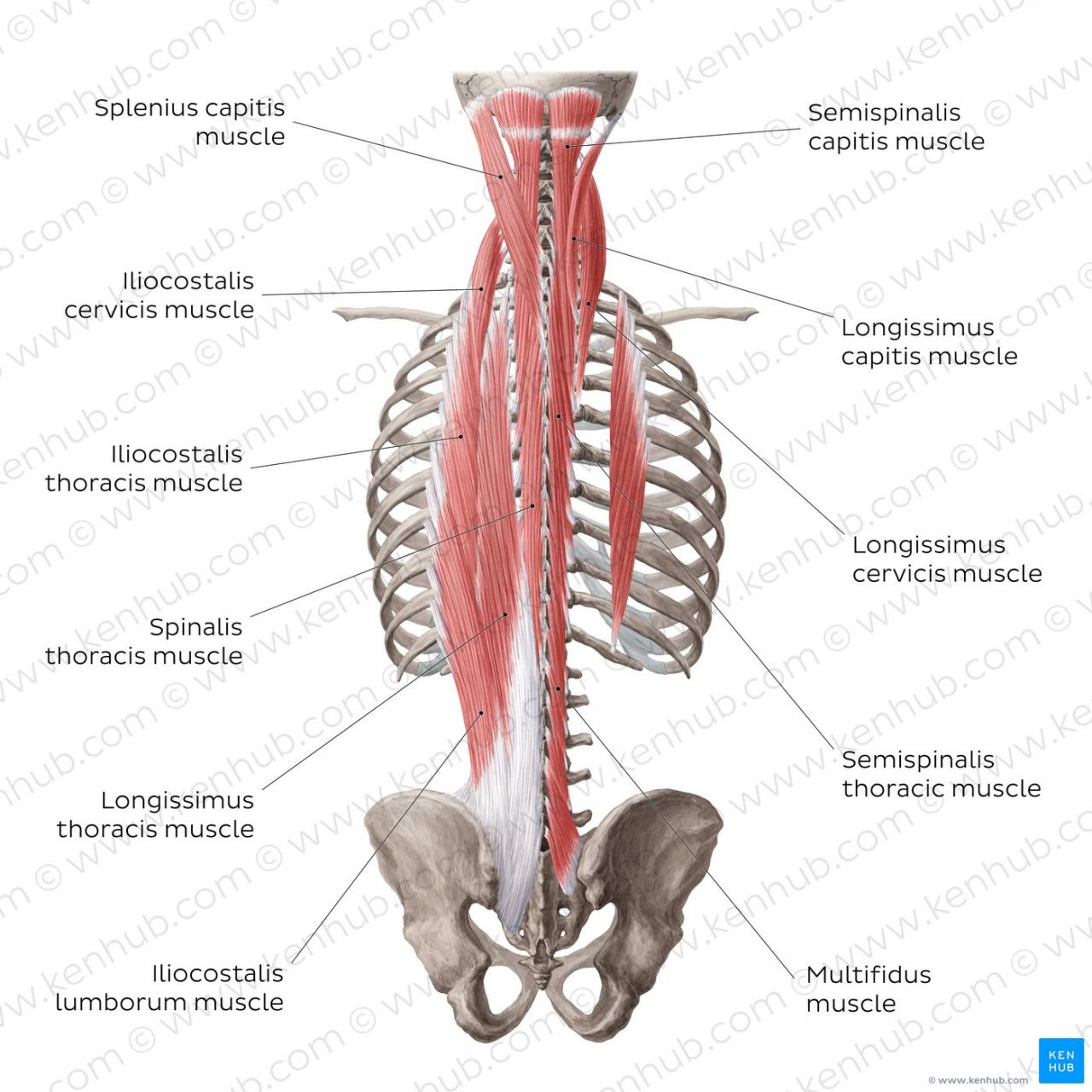
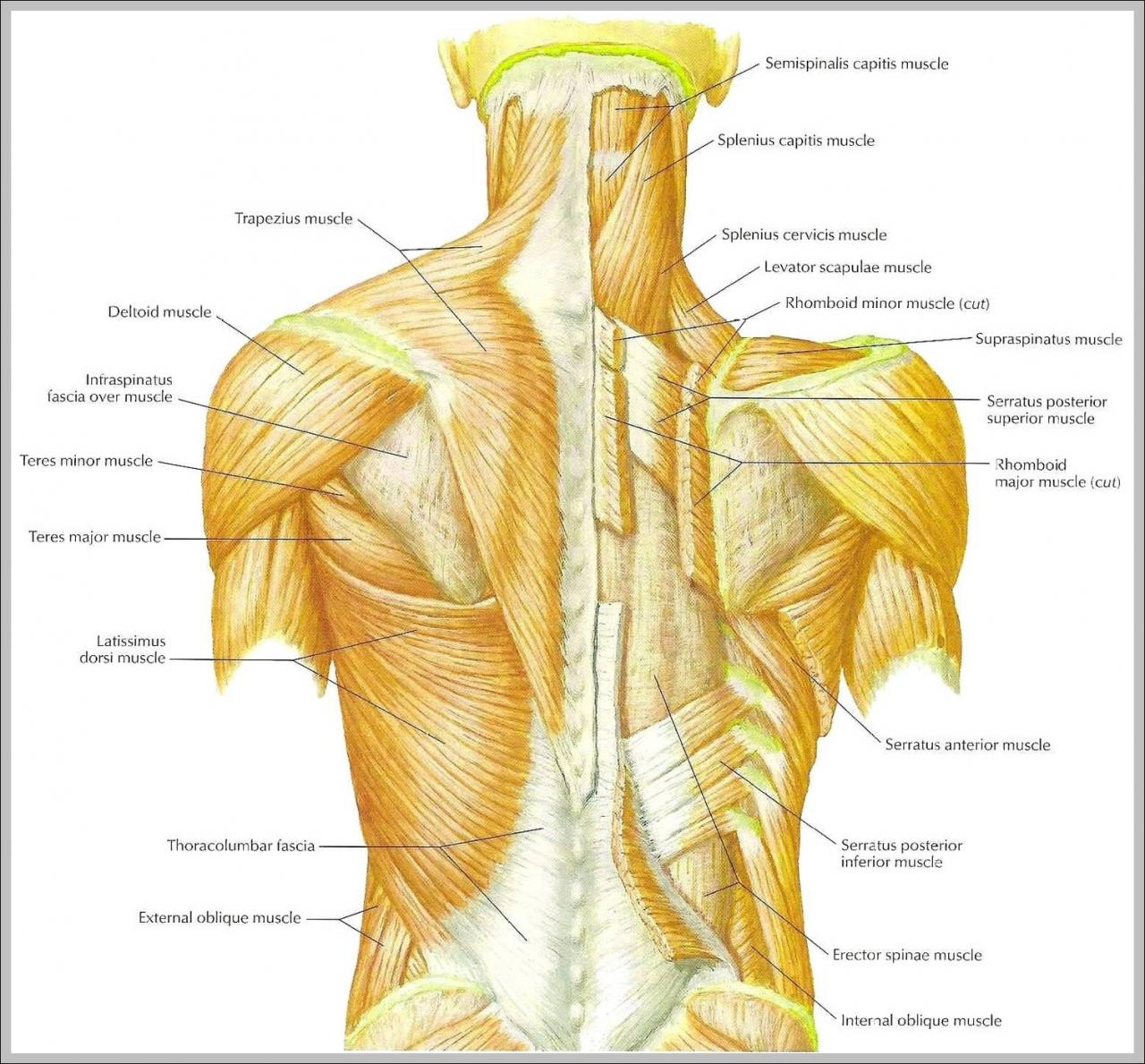
Major Back Muscle Groups
- Latissimus Dorsi:The largest and most superficial back muscle, it extends from the lower spine to the humerus bone in the arm, facilitating arm extension, adduction, and internal rotation.
- Trapezius:A triangular muscle that covers the upper back and neck, it assists in shoulder shrugging, head extension, and scapula movement.
- Rhomboids:Located between the shoulder blades, these muscles retract the scapulae, bringing them closer to the spine.
- Erector Spinae:A group of deep back muscles that run along the spine, they are responsible for spinal extension, lateral flexion, and rotation.
Role in Posture, Balance, and Spinal Stability
The back muscles play a pivotal role in maintaining proper posture, ensuring balance, and stabilizing the spine. They work together to keep the body upright, prevent slouching, and protect the spine from excessive movement or strain.
Exercises for Back Muscle Development
To effectively develop the back muscles, a well-rounded exercise program is essential. Here are some compound exercises that target major back muscle groups:
Compound Exercises
- Pull-ups:A classic exercise that primarily targets the latissimus dorsi, biceps, and forearms.
- Rows:Various types of rows, such as barbell rows, dumbbell rows, and cable rows, engage the latissimus dorsi, trapezius, and rhomboids.
- Deadlifts:A full-body exercise that heavily involves the erector spinae and hamstrings.
Proper Form and Technique
Proper form is crucial to maximize results and minimize injury risk. Focus on engaging the back muscles by retracting the shoulder blades and keeping the spine straight. Avoid using excessive momentum or arching the lower back.
Common Back Muscle Injuries and Prevention
Back muscle injuries can range from minor strains to more severe conditions. Here are some common injuries and preventative measures:
Common Injuries
- Strains:Overstretching or tearing of muscle fibers, causing pain and stiffness.
- Sprains:Ligament tears, leading to joint pain and instability.
- Herniated Discs:Displacement of the soft, cushioning discs between vertebrae, causing pain, numbness, or weakness.
Preventative Measures, Back muscles
- Proper Lifting Techniques:Use proper form when lifting weights or objects to avoid strain.
- Stretching:Regularly stretch the back muscles to improve flexibility and reduce tension.
- Maintaining a Healthy Weight:Excess weight puts strain on the back muscles.
Nutrition for Back Muscle Growth and Recovery
Nutrition plays a vital role in supporting back muscle development and recovery. Here’s a sample meal plan:
Sample Meal Plan
- Breakfast:Oatmeal with protein powder, berries, and nuts
- Lunch:Grilled chicken salad with brown rice and vegetables
- Dinner:Salmon with roasted vegetables and quinoa
- Snacks:Greek yogurt, protein bars, or fruit
Essential Nutrients
- Protein:Essential for muscle growth and repair.
- Carbohydrates:Provide energy for workouts.
- Healthy Fats:Support hormone production and muscle recovery.
Advanced Techniques for Back Muscle Development
For experienced lifters, advanced training techniques can enhance back muscle growth. However, these techniques should be used with caution:
Advanced Techniques
- Drop Sets:Reducing the weight after reaching failure to continue the set.
- Supersets:Performing two exercises back-to-back with minimal rest.
- Forced Reps:Assisted repetitions beyond muscle failure.
Benefits and Risks
Advanced techniques can intensify workouts and promote muscle growth. However, they also increase the risk of injury if not performed correctly. It’s essential to consult with a qualified trainer before incorporating these techniques.
Last Recap: Back Muscles
In conclusion, back muscles are the foundation of a strong and healthy musculoskeletal system. By understanding their anatomy, engaging in targeted exercises, and providing proper nutrition, we can unlock their full potential and achieve optimal movement, posture, and overall well-being.
Essential Questionnaire
What are the most important back muscle groups?
The latissimus dorsi, trapezius, rhomboids, and erector spinae are the key back muscle groups responsible for movement, posture, and spinal stability.
How can I prevent back muscle injuries?
Proper lifting techniques, stretching, maintaining a healthy weight, and avoiding excessive strain can help minimize the risk of back muscle injuries.
What is the best exercise for back muscle growth?
Compound exercises like pull-ups, rows, and deadlifts effectively target multiple back muscle groups, promoting overall growth and strength.






